So, to clarify, what is a private cloud? It’s called a single-tenant setting since each user’s needs are met by a unique allocation of system resources. In contrast to the public cloud, where resources are shared across many users, the private cloud is exclusive to the corporation or organisation using it. These dedicated resources may be managed and hosted in a number of different ways.
A hosted private cloud is one that is provided by a third party in an off-site datacentre. A client-hosted private cloud is one that is installed on client premises and makes use of client IT resources; and a private cloud built on the architecture of a cloud provider is still another option. Private cloud infrastructures commonly use virtualization technologies to pool the available hardware resources into a shared pool to which users have isolated access.
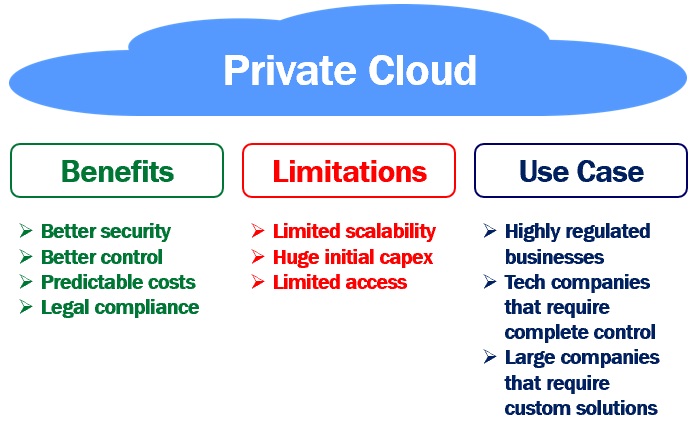
What are the benefits of using a private cloud?
Customers choose a private cloud because it offers the same degree of security and management as their own in-house IT infrastructure, plus the added peace of mind that comes with knowing that only authorised users will ever be able to access their data. Companies with a need to comply with data privacy or regulatory duties, such as those in the banking and financial sector, the government, the healthcare sector, and others, may find this useful.
Installed behind Firewall
Private clouds are often installed behind a firewall, which not only increases network security but also improves speed. Application performance in a private cloud is more stable since it does not rely on shared network resources or hardware with other users. The opposite is true with the public cloud. The public cloud’s metered and unpredictable high monthly usage and storage fees are not applicable here. Instead, monthly costs tend to remain stable regardless of the number of active jobs or the amount of data sent.
Last but not least, compared to the public cloud’s unpredictable monthly billing charges, a private cloud’s higher degree of customisation and ability to yield superior long-term savings are clear advantages. Using a hosted private cloud service allows businesses to save money on expensive hardware. This service takes use of cutting-edge technology and is based on a leasing model for the use of its hardware.
With a private cloud, control is less of an issue
Given that private clouds often reside in privately hosted environments, users have more control over their data, applications, and general infrastructure. Private clouds are advantageous because they allow users to access resources whenever they need them. This allows businesses to handle massive workloads and has the scalability to add additional processing power as needed. Virtualization’s efficiency in using resources is a result of its design. This allows for the possibility of shifting workloads to idle servers in order to maximise resource utilisation.
Customisation
A private cloud may be highly tailored to the needs of an individual business since it is built from the ground up for that business and employs its own unique hardware. This removes any restrictions that would have prevented you from using a public cloud.